
Come Here in Morse Code: Meaning, Pattern & Usage
What Does “Come Here” Mean in Morse Code? “Come here” in Morse code is the Morse representation of a directive

What Does “Come Here” Mean in Morse Code? “Come here” in Morse code is the Morse representation of a directive

What Does “How Are You” Mean in Morse Code? “How are you” in Morse code is the Morse representation of
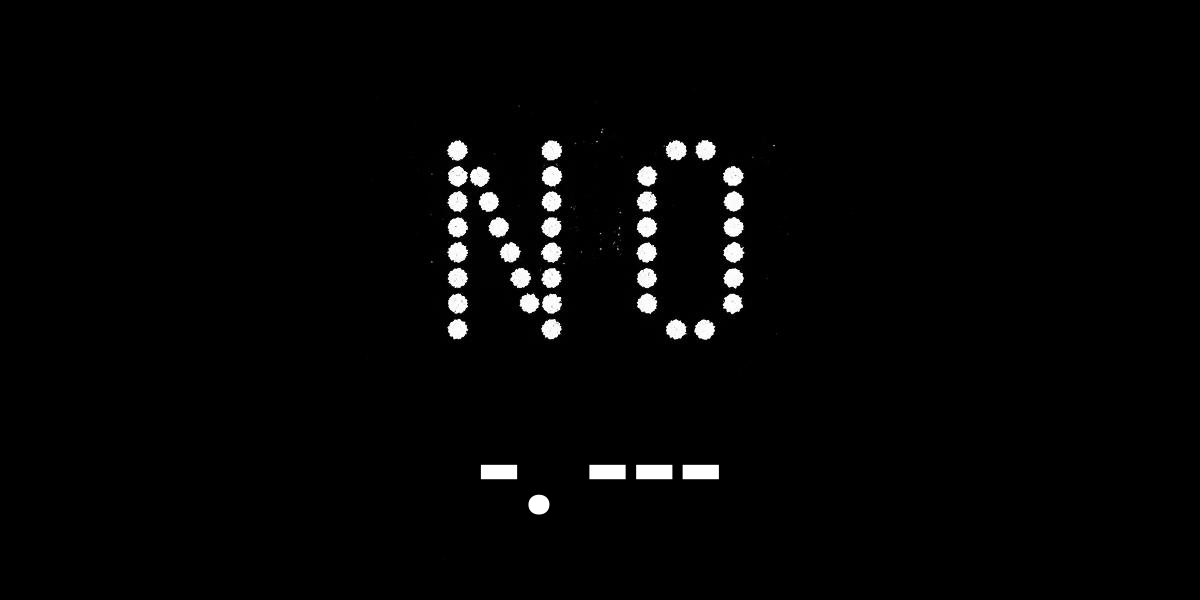
What Is “No” in Morse Code? “No” in Morse code is the Morse representation of the word NO, commonly used

What Is “Yes” in Morse Code? “Yes” in Morse code is the Morse representation of the affirmative word YES, commonly

What Does Emergency Mean in Morse Code? “Emergency” in Morse code refers to communicating an urgent situation using internationally recognized

What Does “Where Are You” Mean in Morse Code? “Where are you” in Morse code is the Morse representation of

What Is “Good Night” in Morse Code? “Good Night” in Morse code represents the common farewell phrase, encoded using dots

What Is “Good Morning” in Morse Code? “Good Morning” in Morse code represents the standard greeting used to wish someone

What Is “Thank You” in Morse Code? “Thank You” in Morse code is the representation of the phrase used to

What Is “I Love You” in Morse Code? “I Love You” in Morse code is a popular phrase used to
Learning Morse code doesn’t have to be complicated. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to improve your speed and accuracy, InMorseCode gives you everything you need to understand, read, send, and practice Morse code using modern online tools.
This page is your central learning hub. You’ll find clear explanations, structured learning paths, and direct access to our Morse code translator, generator, and decoder—all built to help you master dots and dashes efficiently.
Morse code is a system of communication that represents letters, numbers, and symbols using short signals (dots) and long signals (dashes). It was originally developed for telegraph communication but is still used today in amateur radio, aviation, emergency signaling, and education.
Instead of visual characters, Morse code relies on rhythm and timing, making it usable through sound, light, or physical signals. Because of this flexibility, it remains one of the most reliable communication systems ever created.
At the core of Morse code is a standardized alphabet that includes:
Each character is made from a unique pattern of dots and dashes. Learning these patterns helps you recognize Morse code quickly without translating character by character.
👉 Explore the full references:
You can also instantly convert any text into Morse using the InMorseCode translator to see how characters are structured.
Morse code follows precise timing rules that give it a recognizable rhythm:
Correct spacing is just as important as the signals themselves. This timing system ensures that Morse code can be understood clearly across different devices and transmission methods.
To hear accurate timing in action, use the Morse code generator with adjustable speed settings.
InMorseCode follows International Morse Code, the globally accepted standard defined by the ITU-R. This standard ensures that Morse code is:
Unlike American (Railroad) Morse code—which is now obsolete—International Morse code uses only dots and dashes with fixed timing. All modern Morse code translators and decoders rely on this standard.
Learning Morse code is easiest when you focus on sound patterns, not counting dots and dashes. Two proven methods are widely used:
This method teaches Morse code at full character speed from the beginning, adding new characters only after you reach high accuracy. It prevents slow-learning habits and builds instant recognition.
Farnsworth spacing keeps characters fast but increases the space between them. This makes learning easier while still training your brain to recognize correct rhythms.
Both methods are fully supported by InMorseCode’s generator, allowing you to control character speed and overall pace.
Reading Morse code means recognizing patterns, whether they appear as written symbols, audio tones, or flashing lights.
Tips for faster reading:
You can practice visual recognition or audio decoding using the Morse code decoder to verify accuracy.
Proper Morse code writing follows standard formatting rules:
InMorseCode accepts multiple formats and automatically outputs clean, standardized Morse code, making it ideal for learning and practice.
Morse code can be sent in many ways:
Good sending depends on consistent timing and spacing, not speed. The Morse code generator produces perfectly timed signals, helping you develop strong sending habits without mistakes.
Receiving Morse code (also called “copying”) involves listening to signals and converting them back into text. Strong receiving skills come from:
The InMorseCode decoder helps you practice by checking decoded text and identifying spacing or rhythm errors.
The fastest way to learn is through active practice. With InMorseCode, you can:
Everything works directly in your browser—no downloads required.
Morse code is still valuable for:
It’s a skill that combines logic, rhythm, and focus—and once learned, it’s never forgotten.
Yes. It’s widely used in amateur radio, aviation signals, and emergency communication.
Most beginners can recognize basic letters within a few weeks with daily practice.
Learning by sound using the Koch or Farnsworth method is the most effective approach.
Yes. International Morse code is globally standardized.
Ready to practice?
Use InMorseCode’s Morse code translator, generator, and decoder to apply everything you’ve learned and build real skill—step by step.